Mobile Development Team: Build High-Performing Teams 40% Faster

Assembling Your Mobile Development Team
40% of mobile projects miss deadlines due to late hiring decisions. Building a mobile team is about more than listing job titles. You need the right specialists at the right moment to keep development humming and budgets in check.
Core Roles At A Glance
Here’s a snapshot of essential mobile development team roles and when to bring each expert onboard.
| Role | Primary Outcome | When to Add |
|---|---|---|
| Project Manager | Clear roadmap | Project kickoff |
| UI/UX Designer | Intuitive flows | Prototype stage |
| iOS Developer | Native performance | iOS MVP |
| Android Developer | Platform stability | Android MVP |
| QA Specialist | Defect detection | First builds |
| DevOps Engineer | Automated releases | Pre-launch |
This table helps you spot missing skills early, so no one is left waiting for instructions—and nobody’s salary goes to waste.
Staggered Hiring In Practice
On one fintech project I saw, hiring a DevOps engineer before QA slashed release cycles by 40%. The CI/CD pipeline became bulletproof, and downtime dropped sharply.
Key benefits include:
- Automated pipelines that catch manual slip-ups
- Early QA involvement to flag regressions before feature freeze
- Designer input from day one to avoid late-stage UX overhauls
Balancing Platforms
Cross-platform frameworks like React Native accelerate delivery across iOS and Android. Yet, native engineers still play a crucial role in catching OS-specific quirks before they become user-facing bugs.
Late UX changes consumed 20% of one sprint and delayed a release.
When roles overlap or arrive too late, teams often spend up to 25% of sprint hours on rework. Use this lineup as a quick risk checkpoint before launch.
Timing And Trends
By 2025, mobile installs may skyrocket to 299 billion, up from 257 billion in 2023. Google Play wins on volume; the App Store leads in spend per user.
For deeper insights, see our analysis on Tekrevol.
This surge makes cross-platform agility nonnegotiable. If you want to see how large organizations structure their mobile teams, check out our guide on enterprise mobile applications.
Snapshot Recap
With roles mapped and timing dialed in, you can audit your team, close gaps, and avoid last-minute scrambles. Next, we’ll unpack each function with hands-on tips, vendor checklists, and real-world examples.
Define Mobile Development Team Roles
Assigning clear roles in your mobile squad prevents confusion and keeps everyone moving in sync. Teams that know exactly who owns each task deliver features faster and with fewer overlaps.
Whether you’re in a seed-stage startup or a large enterprise, a mix of Project Managers, UI/UX Designers, native Engineers, QA Specialists, and DevOps experts hits all the key touchpoints.
- Project Manager drives the roadmap and handles stakeholder updates.
- UI/UX Designer sketches flows, builds prototypes and runs user tests.
- iOS Engineer writes Swift or Objective-C for seamless Apple integrations.
- Android Engineer crafts Kotlin or Java modules and ensures Play Store compliance.
- QA Specialist builds automated test suites and logs defects.
- DevOps Engineer configures CI/CD pipelines and keeps the infrastructure humming.
Key Mobile Development Team Roles
A Project Manager in a mobile context bridges technical work and strategic goals. They track sprint progress, manage risks, and keep communication channels open.
Designers turn complex requirements into clickable screens. In one fintech startup, their early UI mockups slashed post-launch rework by 30%.
iOS and Android engineers tackle platform quirks and OS updates. A gaming company dropped crash rates by 40% after dedicating experts to each platform.
QA specialists step in before every major build. Their early bug hunts free developers to focus on new features without backtracking.
DevOps pros automate every stage of the release cycle. A retail client went from 12 manual steps down to 2 in a single sprint.
Early DevOps involvement can slash release cycles by 50%, minimizing downtime and manual errors.
Mobile Team Role Breakdown
Below is a side-by-side view of each core function, their main focus areas, and how many people you’ll typically need for a well-rounded team.
| Role | Responsibility | Typical Headcount |
|---|---|---|
| Project Manager | Roadmap, sprint planning, stakeholder updates | 1 per 4–6 engineers |
| UI/UX Designer | Wireframes, prototypes, user testing | 1 per 3–5 engineers |
| iOS Engineer | Native feature development, OS integration | 1–2 for MVP, 3+ for scale |
| Android Engineer | Platform modules, Play Store compliance | 1–2 for MVP, 3+ for scale |
| QA Specialist | Automation scripts, manual testing, regression | 1 per 3 engineers |
| DevOps Engineer | CI/CD pipelines, monitoring, cloud config | 1 for team < 6, 2+ for 10+ |
Use this breakdown when you’re sizing up a new project or benchmarking against industry norms.
Sizing Your Team Per Stage
Early prototypes often thrive with a lean crew. In a seed-funded app, 4 contributors—PM, designer, engineer, QA—launched a usable MVP in 8 weeks.
As you grow, add specialists to avoid bottlenecks. Mid-stage teams usually span 8–12 people, splitting iOS and Android work to boost parallel delivery.
Enterprise rollouts call for dedicated subteams. You might bring in separate QA squads, a design-ops lead, and an additional DevOps expert to handle high-volume testing.
- Seed Stage: 4–6 roles cover core needs.
- Series A: 6–10 roles split across priorities.
- Enterprise: 10+ roles with specialized subteams.
When budgets tighten, postpone noncritical hires like design ops until traffic metrics confirm runway.
Blending Skillsets For Efficiency
Having cross-functional skills on your team speeds up handoffs. An engineer who knows both Kotlin and Jetpack Compose can fill gaps when your Android lead is tied up.
Teaching designers basic prototyping cuts iteration time. One travel startup shaved 25% off its design-to-dev cycle by training engineers in Figma.
Pairing QA with DevOps drives test automation into the pipeline itself. In a healthcare project, this collaboration lifted coverage to 85% in just two sprints.
Creating a resilient mobile team means overlapping expertise so no one area becomes a single point of failure.
Summary Of Roles
- Project Managers keep vision aligned with delivery.
- UI/UX Designers validate flows with real users early.
- Native Engineers ensure performance and platform stability.
- QA Specialists install quality gates before every release.
- DevOps Engineers automate deployments and monitor live systems.
This structure scales from lean startups to global enterprises. Regularly track KPIs like cycle time and defect rate, then adjust roles proactively when metrics slip to keep your mobile team on course.
Decide Between In-House And Partnership Models
Choosing between building a mobile development team internally or bringing on an external partner boils down to trade-offs around cost, control, speed and risk. In some cases—like enterprise finance—deep domain expertise pushes companies toward hiring full-time talent. In others, such as fast-moving gaming startups, a specialized partner can shave months off a launch.
Mobile app revenues reached $935 billion in 2024, and Q1 2025 consumer spend already hit $40 billion worldwide. Apple’s App Store brought in $21.5 billion versus Google Play’s $12.1 billion, showing iOS users still outspend Android despite fewer downloads. You can dive deeper into these trends in the full research here.
Revenue Trends Visual
This chart makes it clear: iOS monetization strength should factor into your investment choices.
In-House Vs Partnership Comparison
Below is a quick-reference table to weigh the core differences between hiring your own team and partnering with an outside firm.
| Criteria | In-House | Partnership |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | $90k–$130k per mobile engineer/year | $100k–$200k per project phase |
| Time To Launch | 3–6 months for hiring and onboarding | 2–4 weeks to ramp up resources |
| Control | Full IP ownership, direct management | Shared governance, fixed scope |
| Scalability | Predictable headcount increases | Flexible scaling on demand |
| Risk Profile | Turnover, training overhead | Vendor dependency, scope drift |
Use this snapshot to align your decision with budget constraints and growth targets.
Key Risk Checkpoints
Watch for these red flags whether you go in-house or partner:
- Talent Drain: High churn stalls roadmaps. Aim for less than 10% annual turnover.
- Scope Creep: Extra features can blow budgets. Lock in a clear change-request process.
- Hidden Fees: Some vendors tack on surprise support charges. Demand transparent line-item pricing.
- IP Leakage: Shared code can expose trade secrets. Insist on iron-clad ownership clauses.
Case Study Examples
A regional bank built out an internal crew of five mobile engineers at roughly $120k annually. They launched a secure trading app in seven months, fully integrated with legacy systems.
Meanwhile, an indie gaming studio hired a partner to prototype AR features in just six weeks for $80k, driving a 25% lift in user retention within 30 days.
These examples underscore the higher upfront investment of in-house teams versus the rapid, cost-effective bursts of innovation you get with partners.
When To Lean In-House
Internal teams make sense when you need:
- Deep integration with existing platforms
- Strict regulatory compliance and top-tier data security
- Guaranteed long-term cost efficiency after the two-year mark
When To Opt For Partnership
Bring in an external expert if you’re looking for:
- Lightning-fast pilot launches under tight deadlines
- Specialized skills like AR/VR or advanced analytics
- The flexibility to handle seasonal spikes without headcount risk
Expert Insight
Partnering shaved six weeks off one gaming MVP launch.
Balancing build versus buy isn’t one-size-fits-all. Map out your strategic goals, run through the risks and let this framework guide whether you invest in an internal squad or tap into a seasoned external team.
Evaluate Vendors With A Checklist
Choosing the right development partner can set your project up for success—or become its biggest hurdle. A detailed checklist makes sure you don’t overlook anything when it’s time to sign on the dotted line.
Vendor Due Diligence Essentials
Kick off your evaluation by digging into corporate records and client references. Ask for case studies in your industry so you can see real outcomes.
Then dive into technical vetting. Review snippets of their codebase. Map out the proposed architecture. Confirm they follow secure development practices and maintain clear, up-to-date documentation.
- Corporate Records: registry status, credit history, litigation background
- Communication: average response times, English fluency, collaboration tool usage
- Compliance: GDPR alignment, SOC 2 coverage, relevant ISO certifications
- Pricing: fixed bids, time & materials, subscription tiers
Communication Best Practices
Transparent communication is the glue that holds teams together. Identify primary contacts, define escalation paths and agree on meeting rhythms from the outset.
- Weekly syncs to track milestones and unblock issues
- Shared dashboards for real-time project visibility
- Centralized decision log for approvals and change requests
Scoring Vendor Responses
Objective scoring cuts through bias. Assign weights across categories—technical expertise, cost transparency and cultural fit—to see clear trade-offs.
A uniform RFP template ensures each vendor addresses the same questions. That way, side-by-side comparisons are straightforward.
“Scoring reduces bias and reveals trade-offs clearly,” says a Senior PM with eight years in mobile projects.
A common breakdown is 30% cost, 40% technical fit and 30% cultural alignment. Adjust the ratios based on what matters most for your initiative.
Decision Tree For Model Choice
Balancing budget against control often drives the in-house vs. partner decision. The diagram below highlights typical scenarios.
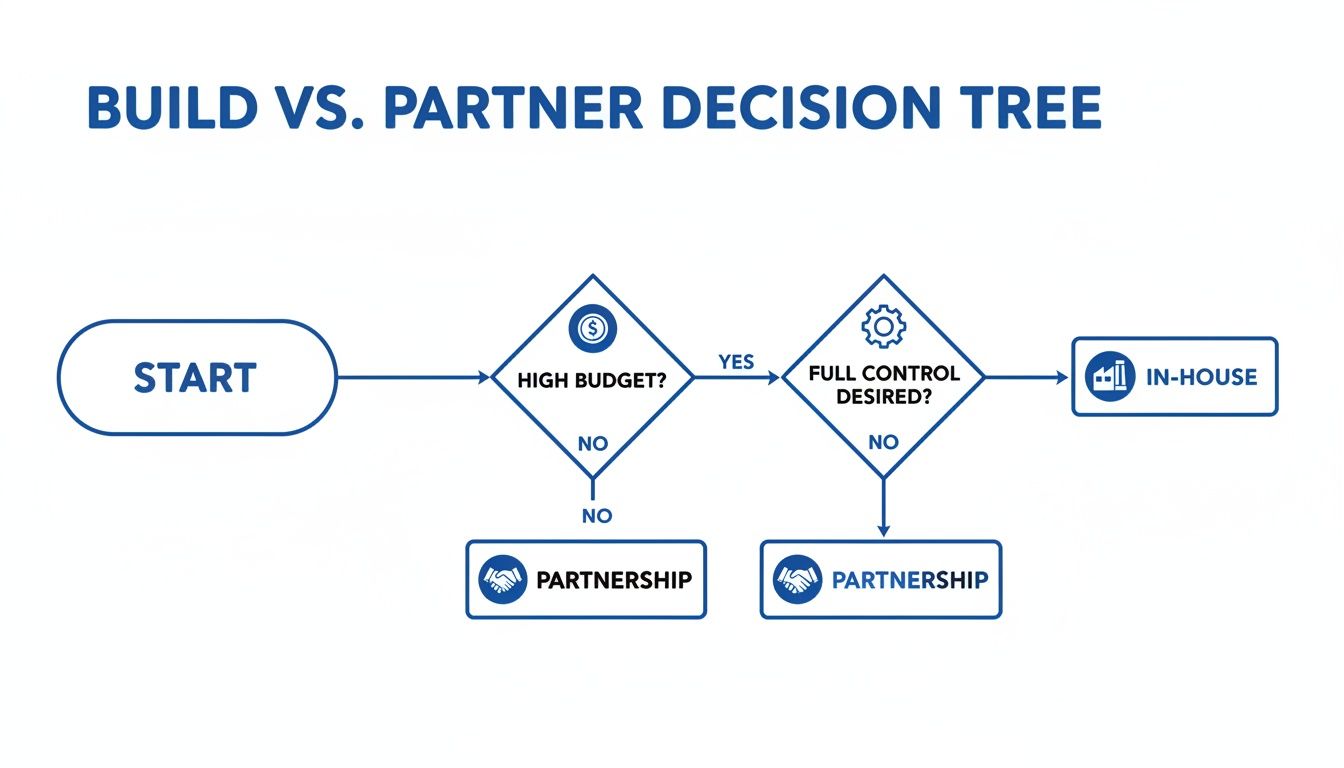
When budgets are healthy, building internally can safeguard IP and governance. Tight budgets and a need for speed tend to favor an external partnership model.
Pilot Projects And KPIs
Before committing to a full engagement, run a focused pilot for four to six weeks. This reveals real delivery cadence and how well features align with your vision.
Agree on metrics in advance. Typical KPIs include delivery velocity, defect density and user retention.
- Define acceptance criteria and plan a demo at pilot end
- Hold daily stand-ups and weekly reviews to monitor progress
- Track time per feature to understand resourcing needs
Conclude with a joint workshop to capture lessons learned and refine the roadmap for the next phase.
Below is a simplified org chart showing common vendor-side roles:
| Role | Vendor Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Engagement Manager | Stakeholder alignment and reporting |
| Solution Architect | Technical design and integration |
| Mobile Engineers | Development, code quality and tests |
| QA Analysts | Test planning and automation |
| Project Lead | Scope management and delivery |
You might be interested in our detailed vendor due diligence checklist for fill-in-the-blank templates and scoring approaches.
Pricing Models And Compliance Checks
Compare fixed-price, time & materials or subscription options. Tie payments to clear milestones—this guards against cost overruns.
Confirm all compliance requirements—GDPR, SOC 2 and any industry-specific standards—are fully met. Verify certificates and data residency controls.
- North America: $100–$140 per hour
- Eastern Europe: $40–$60 per hour
- APAC Region: $30–$50 per hour
Insist on SLAs covering uptime, performance and bug-fix turnaround. Penalties for missed targets keep everyone accountable.
When Not To Proceed
Red flags deserve your attention. If a vendor lacks domain expertise or falls short on core compliance, pause the process.
Slow responses, opaque pricing or no clear roadmap often signal deeper issues. If pilot deliverables repeatedly miss deadlines, it’s time to reevaluate.
Final Review And Contracting
Collate your scores, pilot feedback and compliance checks into a single dossier. Engage legal and procurement early to draft SLAs and contracts before full kickoff.
Keep refining your checklist after every evaluation to stay sharp.
Sample RFP Scorecard
A color-coded scorecard makes comparisons instant. Mark low performers in red and top contenders in green for quick clarity.
- Vendor Name
- Technical Score
- Cost Score
- Cultural Fit Score
- Total Score
Set score thresholds, finalize your shortlist and present a concise summary to executives. Outline trade-offs clearly and recommend next steps for procurement or contracting. Document every decision to maintain an audit trail and shared accountability.
Identify Mobile Team Pitfalls And When To Pivot
Sometimes the biggest roadblocks in mobile development aren’t in the code but in the team itself. Unplanned feature creep or mismatched skills can stall progress—and early detection often saves 30% in rework costs.
For any mobile development team, spotting budget or timeline risks before they escalate is vital. Knowing the right moment to change course separates a smooth launch from an expensive delay.
Common warning signs often get buried under daily tasks. Watch out for:
- Feature Creep: Unscheduled work slipping into sprints
- User Retention: DAU/MAU dropping by more than 20% in the first month
- Skill Gaps: Lack of expertise for new frameworks or local market nuances
Key Insight: A 25% spike in defect tickets in a single sprint usually means technical debt is spiraling.
When the market is crowded, a generic app simply gets lost. Teams may find themselves stripping features back or abandoning niche segments entirely. Often, it’s about choosing the right moment to double down or step aside.
Without rigorous backlog grooming, unchecked feature creep can inflate your scope by over 40%. And slipping retention rates tend to hint that you’re off-target with your core functionality.
Spotting Feature Creep Early
It’s easier to course-correct when you catch scope bloat at the door. Look for:
- Tickets piling up right after sprint planning
- Daily stand-ups dominated by last-minute feature requests
- A sudden rise in unestimated tasks during backlog refinement
Platform updates will shine a light on skill gaps. Missing in-house expertise can stall releases for weeks. In emerging markets, cultural missteps or language barriers make local specialists a worthwhile investment.
Quick fixes pile on technical debt. Each time you patch instead of refactor, future features become riskier and slower to deliver.
Real Case Of Pivot Decision
Here’s a snapshot of a real-world trigger point:
| Scenario | Action |
|---|---|
| App slowed by legacy SDK conflicts | Pivot to shim layer |
| Market overcrowding in fitness apps | Scrap and repurpose UI |
A mid-sized health-tracking app saw engagement fall 25% after SDK conflicts caused crashes. Rather than chase every bug, the team rebuilt key modules in React Native.
In 2025, the global app economy is on track to top $1 trillion by 2034—driven by lean squads of 6–12 developers handling 299 billion downloads. Get 2025 mobile team statistics
This chart underlines how small, agile teams manage enormous scale. With a global talent squeeze, you’ll often tap contractors who speak local languages or specialize in microservices.
Lightweight Validation Strategies
Small experiments stop big failures. Getting quick feedback keeps you from chasing dead ends and preserves your budget.
- Low-Code Platforms: Build clickable flows in hours to test user journeys
- A/B Tests: Expose small cohorts to two variants and compare retention
- Embedded Surveys: Drop feedback widgets into prototypes for instant reactions
- Pilot Launches: Release a minimal version in a target region to validate performance under real load
For detailed guidance on adapting legacy systems or evaluating vendor paths, check out our guide on application modernization strategies. Learn more about application modernization strategies
Trying micro-prototypes before full builds can reduce wasted effort by 60%.
Pivot Criteria Next Steps
Numbers don’t lie—set clear benchmarks to decide your next move:
- MAU drop > 20% month-over-month
- Crash rate above 2% after major releases
- More than 30% of sprint stories rolling past deadlines
- User acquisition cost rising by 15% or more
Review these checkpoints weekly to choose whether to kill, pivot or double down. Clear thresholds—like a 30% dip in core metrics or 20% feature debt—act as your early-warning system. Capture every pivot decision in writing so you can learn, iterate and improve faster.
Optimize Mobile Development Team Performance
Now that your mobile squad is in place, keeping an eye on performance metrics is the best way to stay on track. These numbers align everyone—from product owners to engineers—and help catch issues long before deadlines.
Key Metrics To Track
- Cycle time: How long it takes to move a user story from ready to done.
- Deployment frequency: The number of releases hitting production each week.
- Crash rate: The share of sessions that end unexpectedly.
- Code review turnaround: Time between a pull request and merged feedback.
- Budget variance: Cost overruns compared to your initial plan.
Together, these figures form a live snapshot of team health.
Real squads use Grafana or Data Studio to plot cycle times, deployment streaks and crash reports in real time.
Sprint Planning Hacks
Short, focused sprints surface potential roadblocks fast and keep teams nimble.
I once worked with a group that trimmed their sprint from three weeks to just ten days. The result? A 22% jump in throughput and a backlog that didn’t roll over releases.
They leaned on planning poker to size work and enforced a strict definition of ready. This cut down guesswork dramatically.
- Keep retrospectives under 30 minutes.
- Rotate facilitators to spark new ideas.
- Refine stories with designers and engineers 24 hours before sprint start.
CI/CD Pipeline Tips
Automating builds and tests stops regressions from sneaking into production.
For iOS, add fastlane commands. For Android, rely on Gradle scripts. One retail client slashed manual release steps from 12 down to 3 by unifying their pipeline.
Embedding tests in the CI flow boosted coverage by 30%—and uncovered flaky code early.
- Fail builds on lint errors to enforce style rules.
- Require at least two approvals on critical pull requests.
- Run nightly performance benchmarks in an isolated sandbox.
“A CI-driven workflow cut our release risk by catching flaky tests before shipping,” says a Lead DevOps Engineer.
Code Review Workflows
A smooth code review process turns feedback into a team-wide learning opportunity.
- Use pull request templates to standardize commit messages and link to tickets.
- Integrate linting with pre-commit hooks so style issues pop up immediately.
- Employ merge queues or GitHub Actions to batch reviews instead of blocking on one-by-one approvals.
Peer reviews not only catch edge-case bugs but also spread domain knowledge across your developers.
Communication Rituals
Regular check-ins keep product, design and engineering in sync.
Whether it’s a daily stand-up or a monthly deep-dive, these touchpoints create clear feedback loops.
- Tiny stand-ups in chat channels for asynchronous status updates.
- A shared Kanban board that’s always visible to stakeholders.
- Brown-bag sessions for tackling complex technical challenges.
Document decisions in a shared log. This prevents debates from resurfacing and captures trade-offs clearly.
| Metric | Healthy Threshold |
|---|---|
| Cycle time | < 7 days |
| Deployment frequency | ≥ 3 per week |
| Crash rate | < 1% |
| Code review turnaround | < 24 hours |
Cost Monitoring Checkpoints
Tag your builds with cost centers so you can see spend per feature in real time.
A fintech team I know capped experimental branches at $5k to avoid runaway cloud bills.
- Audit AWS Cost Explorer each week to spot spikes.
- Track emulator usage so you don’t pay for idle devices.
- Clean up stale feature branches after 14 days of no commits.
If you see costs climbing while velocity drops, pause new features and reevaluate.
Tooling And Integrations
Use rapid feedback tools like HockeyApp or Firebase Crashlytics and connect them to your alerting system.
- Hook Grafana to PagerDuty for 24/7 incident notifications.
- Run cross-repo workflows with GitHub Actions or Jenkins.
- Store CI logs in S3 for easy auditing and quick rollbacks.
Continuous feedback loops anchored in data keep your mobile team agile. Review these KPIs weekly, tweak your processes and share successes (and failures) openly.
Avoid vanity metrics like download counts unless you pair them with retention or revenue numbers. And if meetings start outnumbering code commits, carve out time to automate or drop the low-value gatherings.
Expert Takeaway
Mobile teams that iterate on real data minimize rework and keep budgets under control.
When key metrics dip below your healthy thresholds for three sprints in a row, pause new development and drill into the root causes. If crash rates stay above 2%, bring in a dedicated quality squad before piling on more features.
Tag story points in JIRA with financial labels to calculate cost per feature. That gives you a quick view of outliers and efficiency bottlenecks.
Finally, champion a culture of continuous learning. It’s the single best way to sustain performance gains over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Putting together a mobile development team often sparks the same set of questions for engineering leaders. Here, you’ll find straight-to-the-point advice on squad size, clear role boundaries, vendor vetting and budget checkpoints.
What’s the ideal team size for an MVP launch?
A nimble group of 4–6 core roles usually provides enough firepower without slowing things down.
How do I prevent role overlaps?
Sharp role definitions keep everyone in their lane. For instance, let your UI/UX Designer own the user flows before a single line of code is written, while native engineers focus on platform-specific features.
- Project Manager drives the roadmap and sprint cadence.
- UI/UX Designer validates flows and prototypes ahead of development.
- iOS Engineer and Android Engineer each tackle their respective platforms.
Sizing And Role Clarity
Curious when to bring QA and DevOps onboard? Involving QA early can slash rework by 30%, catching bugs well before launch. And having a DevOps specialist in place pre-launch sets up solid CI/CD pipelines from day one.
Choosing the right vendor? Build a simple scoring model that weighs 30% cost, 40% technical fit and 30% cultural alignment—and don’t skip a trial sprint. It’s your best bet to validate their delivery rhythm.
Expert Insight: A four-week pilot often reveals communication gaps or skill mismatches before you sign a long-term deal.
A winning evaluation flow:
- Map out “must-have” skills in your RFP with crystal-clear success criteria.
- Rate each proposal against your weighted cost, tech and culture metrics.
- Dive into pilot results—look at delivery velocity, defect counts and initial user feedback.
Cost Estimation And Checkpoints
So, what budget should you pencil in? In-house engineers run $90k–$130k per person annually. If you’re leaning on a partner, expect to start around $100k per project phase.
- In-House: $90k–$130k/engineer/year
- Partnership: from $100k per phase
Ready to make defensible choices for your mobile development team? Explore failure analysis, cost benchmarks and partner profiles on Modernization Intel.
Need help with your modernization project?
Get matched with vetted specialists who can help you modernize your APIs, migrate to Kubernetes, or transform legacy systems.
Browse Services